0
1
1
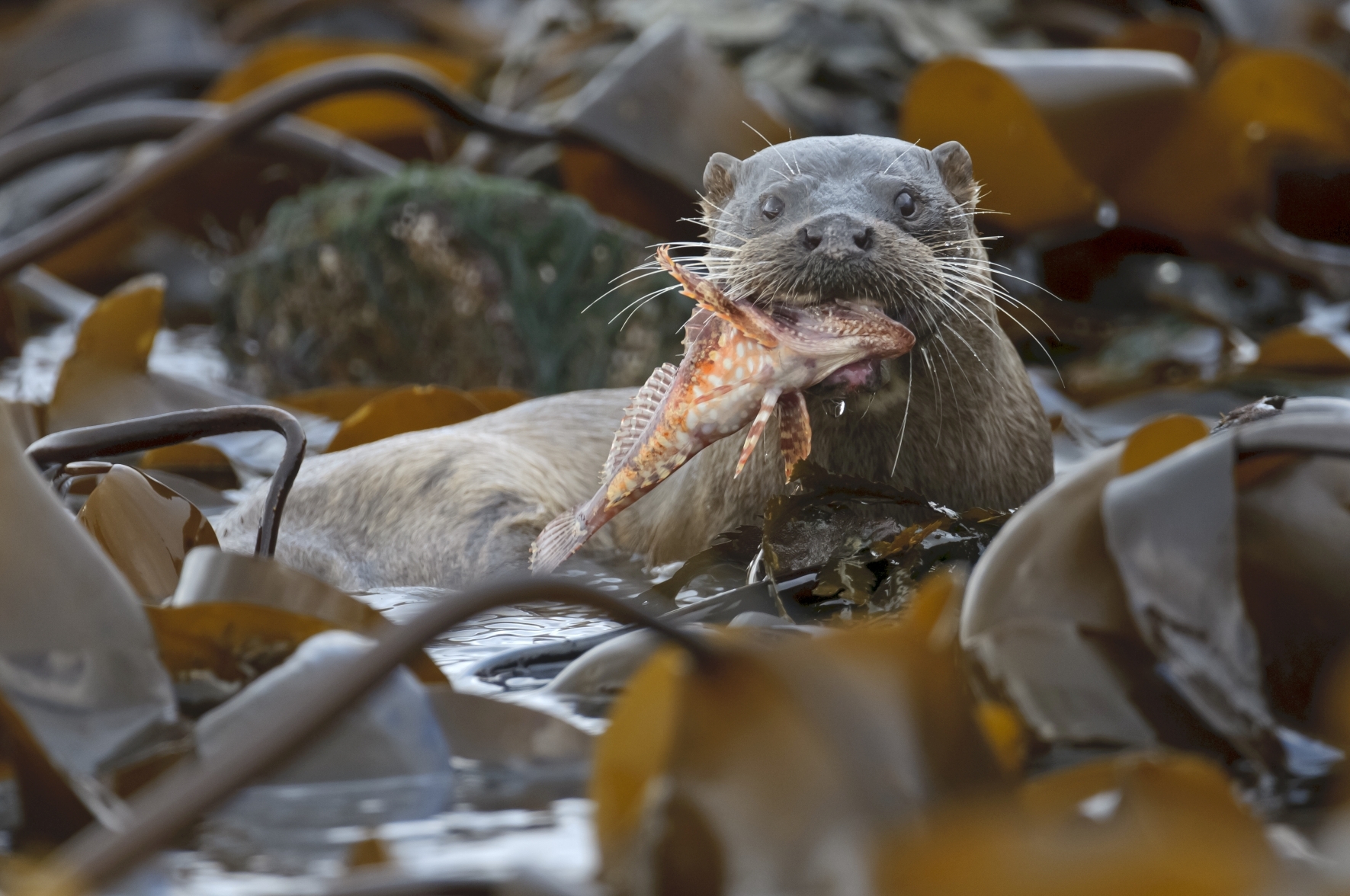
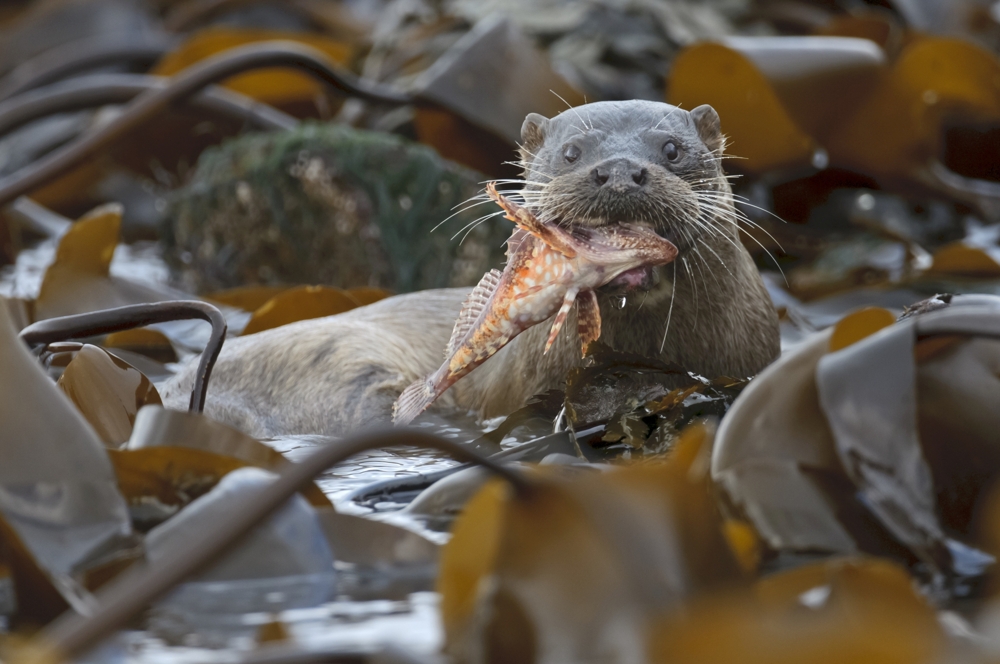
The European mink (Mustela lutreola), also known as the Russian mink, is a semiaquatic species of mustelid native to Europe. It is listed by the IUCN as Critically Endangered due to an ongoing reduction in numbers, having been calculated as declining more than 50% over the past three generations and expected to decline at a rate exceeding 80% over the next three generations. European mink numbers began to shrink during the 19th century, with the species rapidly becoming extinct in some parts of Central Europe. During the 20th century, mink numbers declined all throughout their range, the reasons for which having been hypothesised to be due to a combination of factors, including climate change, competition with (as well as diseases spread by) the introduced American mink, habitat destruction, declines in crayfish numbers and hybridisation with the European polecat. In Central Europe and Finland, the decline preceded the introduction of the American mink, having likely been due to the destruction of river ecosystems, while in Estonia, the decline seems to coincide with the spread of the American mink.
It is similar in colour to the American mink, but is slightly smaller and has a less specialised skull. Despite having a similar name, build and behaviour, the European mink is not closely related to the American mink, being much closer to the European polecat and Siberian weasel (kolonok). The European mink occurs primarily by forest streams unlikely to freeze in winter. It primarily feeds on voles, frogs, fish, crustaceans and insects
It is similar in colour to the American mink, but is slightly smaller and has a less specialised skull. Despite having a similar name, build and behaviour, the European mink is not closely related to the American mink, being much closer to the European polecat and Siberian weasel (kolonok). The European mink occurs primarily by forest streams unlikely to freeze in winter. It primarily feeds on voles, frogs, fish, crustaceans and insects
Source:
реклама