150
11
Let’s face it, everyone loves coffee. The magical black liquid will perk you up in the mornings, has a taste unlike any other, and according to the latest research, offers a wide variety of health benefits to regular drinkers. From the very beginning of people drinking coffee, there have been widespread myths about how awful it is. Luckily for us that enjoy sipping a cup of joe in the morning, almost all of these things have been proven false.
10. Coffee Will Sober You Up
The myth about the sobering power of coffee mostly comes from television shows and movies. When someone is very drunk and needs to sober up, coffee consumption is usually offered as a quick and easy solution. The reality is that coffee will not help you get sober faster. In fact, research shows those who mix coffee and alcohol are likely to have car accidents or drink more heavily since drinking caffeine will trick your brain into thinking you’re closer to sobriety than you actually are. Sorry, coffee-loving weekend drinkers – you’re going to have to wait for the alcohol to make its way out of your system on its own.
9. Coffee/Caffeine Dehydrates You
This is a common thing all of us coffee lovers have probably heard at one time or another. But what if I told you that it’s completely bogus, and coffee actually hydrates you? Caffeinated beverages do behave as mild diuretics, but the water contained in the coffee more than makes up for the small amount of loss. The average cup of coffee is about 98.7% water (the rest is that delicious essence of bean). All studies unanimously show that caffeinated beverages such as coffee, tea, soda, etc., do not cause dehydration. In fact, your daily cup may be contributing to your healthy water intake.
8. Espresso Has More Caffeine Than Drip Coffee
A standard cup of drip-brewed coffee contains more caffeine than a single shot of espresso. We tend to think the opposite, thinking that because the espresso is a more concentrated form of coffee, it must therefore have a higher concentration of caffeine. Technically, this part is true. The average serving of one ounce of espresso contains about 30 to 50 milligrams of caffeine, while one ounce of brewed coffee has between 8 to 15 milligrams. But this is not a case where less is more: because most people drink brewed coffee servings of between 8 to 24 ounces, the much larger volume of a regular cup of coffee results in more caffeine content overall.
7. Coffee Will Stunt Your Growth
This is an old one. You might have seen references to it in comic strips, or maybe your grandparents quipped it once or twice. Unfortunately, it’s the old wives’ tales that do seem to linger on forever. No one has ever been able to prove that coffee stunts the growth of children. Yet the urban legend sticks around, with most parents refusing to let their children drink coffee because “it’s unhealthy for kids” all the while they guzzle Coke and Pepsi like there’s no tomorrow. There is no correlation between caffeine intake and growth, bone density, or anything like that. The closest is the fact that caffeinated beverages do reduce calcium absorption, but this has been wildly overstated. The calcium in only one tablespoon of milk is enough to offset eight ounces of coffee. If you already take in enough calcium, you should have nothing to worry about!
6. Coffee is Addictive
Ever tried quitting coffee? Yeah, you get a really bad headache. No doubt, withdrawing from caffeine is not fun. But as unpleasant as that experience may have been, it still doesn’t qualify as an addiction. Coffee simply doesn’t have the same hold on people as alcohol, cigarettes, and hard drugs. Not to mention people who are “addicted” to coffee will not exhibit the same harmful drug-seeking behaviors as true addicts. Unlike those other drugs, coffee also does not have any proven negative effects on your body due to long-term use (in fact most studies claim that coffee is overwhelmingly good for you – more on this later). For these reasons, dependence on caffeine is not considered to be a serious addiction by medical professionals.
5. Coffee Causes Insomnia
Coffee has a relatively short half-life, that is, the time it takes for your body to eliminate half of it. It only takes about 3 to 5 hours for half of the substance to be eliminated. Caffeine also reaches its peak level within 30 to 60 minutes. Now, don’t get me wrong – drinking coffee can disrupt your sleep, but only if you drink it less than about 6 hours before bed. Though keep in mind that the way we react to caffeine is different for each person, and while drinking coffee late at night will probably keep you up, an afternoon cup probably won’t hurt your sleep schedule that much.
4. Dark Roasts Are Stronger and Have More Caffeine
Darker roasts are usually thought of as “stronger” than light ones due to their bold flavor. But flavor alone is not an indication of caffeine content. Though the taste of a dark roast tends to be stronger and richer than a light roast, dark roasts have less caffeine. However, it is also a myth that dark roasts tend to have less because the caffeine is “cooked out” by the roasting process. The truth is very little if any caffeine is lost during the roasting. What actually happens is that a bean loses its mass during the process, and beans that are roasted longer are less dense. Since most people measure out their coffee in scoops, that means light roasts will have more caffeine since they are more dense than darker ones. But if you weigh your coffee portions, darker roasts would have more. Coffee sure can be complicated, huh?
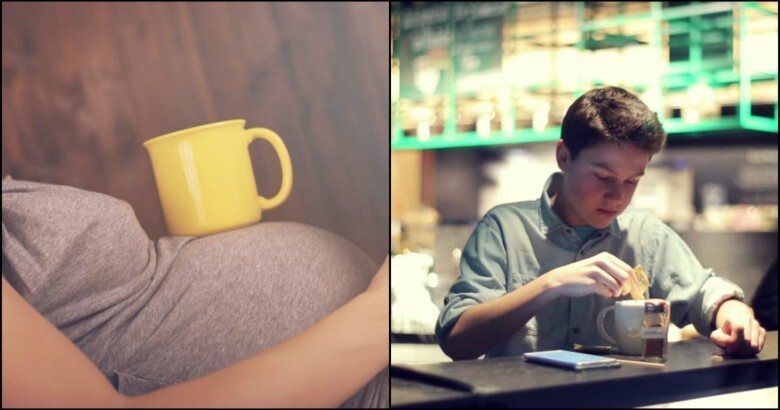
3. Pregnant Women Need To Avoid Coffee
The long and short of it is that studies have found no significant risk to either the mother or the fetus in moderate coffee consumption during pregnancy. We still don’t know a lot about the effects of caffeine during pregnancy, so if you’re pregnant, doctors recommend limiting your intake to about 200 milligrams per day. That’s about one and a half 8-ounce cups of coffee, or one 12-ounce cup of coffee. While coffee consumption in moderation may be a wise course of action during pregnancy, the idea that drinking coffee will lead to birth defects, complications, disorders, or even cause the mother to miscarry (all actual rumors) is simply not supported by any science.
2. Coffee Causes Cancer or Other Diseases
That’s a big, fat nope. Most scientific studies have reached the consensus that coffee is good for you and may actually help prevent certain diseases. Though rumors and urban legends about coffee’s supposed health hazards have haunted the popular drink since its discovery, investigations since then have revealed decreased risk of melanoma, breast cancer, heart disease, Alzheimer’s, reduced mortality risk, and many others. Coffee may also help protect against type II diabetes, Parkinson’s, dementia, and liver disease. To put the nail in the coffin of this old myth, consumption of coffee has not been linked to increased risk of any chronic disease.
1. Coffee Boosts Metabolism/Helps You Lose Weight
Okay, strictly speaking, it is true that coffee does boost your metabolic rate. Caffeine is the most commonly consumed psychoactive substance in the world, and coffee does give us a burst of energy, including to the metabolism. But can coffee help us lose weight in the long-term? Sorry to burst your bubble on this one, but no. Even though coffee will boost your metabolism in the short-term, the one major flaw here is that coffee drinkers get used to the caffeine intake and develop a tolerance over time. While like most things health-related it may depend on the individual, as of now there is no hard science to prove that coffee helps you lose weight.
Source:
Ссылки по теме:
- Biodegradable Coffee Cups Embedded With Seeds
- TOP 10 COOLEST COFFEE TABLES
- Unusual drawings on coffee cups
- Let Your Creativity Soar By Using These Incredible Coffee Mugs.
- Guy Spends 5 Hours Drawing Detailed Map Of Middle-Earth
реклама